to extract .wpress
1. Make sure Node.js installed
node --version2. cd to the directory where .wpess is, then run a command
npx wpress-extract filename.wpressDONE!
to extract .wpress
node --versionnpx wpress-extract filename.wpressDONE!
$ sudo certbot --nginx$ sudo certbot --nginx -d example.com$ sudo certbot certificatesNOTE: check each nginx conf files updated by Certbot
$ sudo certbot delete --cert-name example.com$ sudo certbot certonly --expand --cert-name existingdomain -d existingdomain.com,www.existingdomain.com,new.existingdomain.comIn case, accidentally deleted a certificate, here how to fix.
sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d deletedDomainname.comSince still nginx.conf contain information about the deleted certificate, it need reissue certificate ONLY = certonly flag to avoide nginx error such as:
nginx: [emerg] cannot load certificate "/etc/letsencrypt/live/domainname.com/fullchain.pem": BIO_new_file() failed (SSL: error:80000002:system library::No such file or directory:calling fopen(/etc/letsencrypt/live/domainname.com/fullchain.pem, r) error:10000080:BIO routines::no such file)
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test failedcase: remove a row with FOREIGN_KEY
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECK = 0;
DELETE FROM `tableName` WHERE (id = `idNumber`);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECK = 1;case: reset AUTO_INCREMENT id MAX
ALTER TABLE `tableName` AUTO_INCREMENT = `value`;The ‘value’ is where the AUTO_INCREMENT starts next time.
SELECT @max := MAX(ID) + 1 FROM `tableName`;
PREPARE stmt FROM 'ALTER TABLE `tableName` AUTO_INCREMENT = ?';
EXECUTE stmt USING @max;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt;case: unable to enter `emptyValue` ” to a NULL space. (once rebooted mySQL, run the command)
SET @@global.sql_mode = '';
Finally updated my mentality to Vue 3. I’ve updated my Mac OS from Catalina to Monterey a while ago and started to thinking about software update accordingly. The big one was Node, I’ve been using the version 12 for such a long time, so decided to update to v16. Thanks to nvm, I can switch versions when I needed. And started to try Vue3.
Vue3, Vite server, it’s just amazingly FAST!!! I’m loving it.
> npm init vue@latest
> npm run devSo far, trying to get familiar with update and I’ve encounter an axios issue. I’ve install axios and vue-axios. According to https://stackoverflow.com/questions/68233550/what-is-the-different-between-axios-vue-axios. “vue-axios is just a wrapper, exposing axios to components as this.axios, this.$http, or Vue.axios.”
import axios from "axios";
import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'
app.use(VueAxios, axios);
app.mount("#app");
// with in a component add this
add(payload) {
const path = "URL";
this.axios.post(path, payload)
.then(() => {I’ll update when I noticed something converting from vue2 to VUE3
<svg viewBox="0 0 100 100" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<rect x=0 y=0 width=100 height=100 fill="black" />
<circle cx="20" cy="20" r="20" fill="red" />
</svg>
<svg viewBox="0 0 100 100" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<rect x="0" y="0" width="100" height="100" fill="black"></rect>
<circle cx="20" cy="30" r="20" fill="red">
<animate attributeName="cx" from="0" to="100" dur="2s" repeatCount="indefinite"></animate>
<animate attributeName="cy" from="30" to="100" dur="2s" repeatCount="indefinite"></animate>
</circle>
</svg>
You can use Javascript to manipulate element
var svg = document.getElementById('IDNAME');
and/or CSS
@keyframes
<style>
.wrapper{
height:400px;
width: 400px;
background:#111;
text-align: center;
overflow: hidden;
}
.svg-wrapper {
height: 60px;
margin: 0 auto;
position: relative;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
width: 320px;
}
.shape {
fill: transparent;
stroke-dasharray: 140 540;
stroke-dashoffset: -474;
stroke-width: 8px;
stroke: #19f6e8;
}
.text {
color: #fff;
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
font-size: 22px;
letter-spacing: 8px;
line-height: 32px;
position: relative;
top: -48px;
}
@keyframes draw {
0% {
stroke-dasharray: 140 540;
stroke-dashoffset: -474;
stroke-width: 8px;
}
100% {
stroke-dasharray: 760;
stroke-dashoffset: 0;
stroke-width: 8px;
}
}
.svg-wrapper:hover .shape {
-webkit-animation: 0.5s draw linear forwards;
animation: 0.5s draw linear forwards;
}
</style>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="svg-wrapper">
<svg height="50" width="320" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<rect class="shape" height="60" width="320" />
</svg>
<div class="text">HOVER</div>
</div>
</div>My previous post was to introduce git, this one is for CLI update/note:
$ git init ProjectName.git --bare (create remote empty git repo as origin master to push)
$ git push --set-upstream origin BranchName. (To push the current branch and set the remote as upstream)
$ git push -u origin myBranchName
$ git remote -v (List remote repo)
$ git remote add <name> <url> (add remote repo <name> = “origin”, url = server.com:/where/the/project.git)
$ git checkout --filename.ext (remove the file filename.ext from git)
$ git status (show current status of git, I execute it before git add .)
$ git restore filename.ext (before commit, restore the file to previous status, even file is saved, the content is back to the before)
$ git clean -df projectName (clean up git)
$ git log --oneline --graph (show list of commit.)
$ git reset --hard HEAD (go to current HEAD.)
$ git reset --hard HEAD^ (go back to the 1 commit from current HEAD.)
$ git reset --hard HEAD~2 (go back to the 2 commits from current HEAD.)
$ git reset --hard index (go back to the commit where the index is)
Just encounter an accident, so I’m updating the post.
Accidentally overwritten a file!! OMG. A awesome thing about git is you can retrieve a file or files later. Usually right after you save a file and notice a mistake and Ooops, I shouldn’t save the file, in stead save as different file name. Anyway if you saved and noticed, means you have not git commit the change. So simply:
$ git status (show status what has been modified)
$ git restore fileName (restore the file)
IMPORTANT: Once you notice, you need to change the file name before do git restore, so you can have both.
If you’ve already git add . + committed, you should use
git reset --hard HEAD^ (go back to the 1 commit from current HEAD.)
IMPORTANT: before git reset, always nice to have a current backup somewhere else in local or remote.
find remote branch names
$ git remote -v show origin
pull the remote branch
$ git pull branch-name
Do you know or have you heard “git” or maybe “github”?
Git (/ɡɪt/)[7] is software for tracking changes in any set of files, usually used for coordinating work among programmers collaboratively developing source code during software development. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows (thousands of parallel branches running on different systems).
Even you are not a programmer or computer software/web developer, I think this tool is a super useful. If you only use Word, Excel etc.., anything that you need to save some data as a file, it’s very helpful to manage your project.
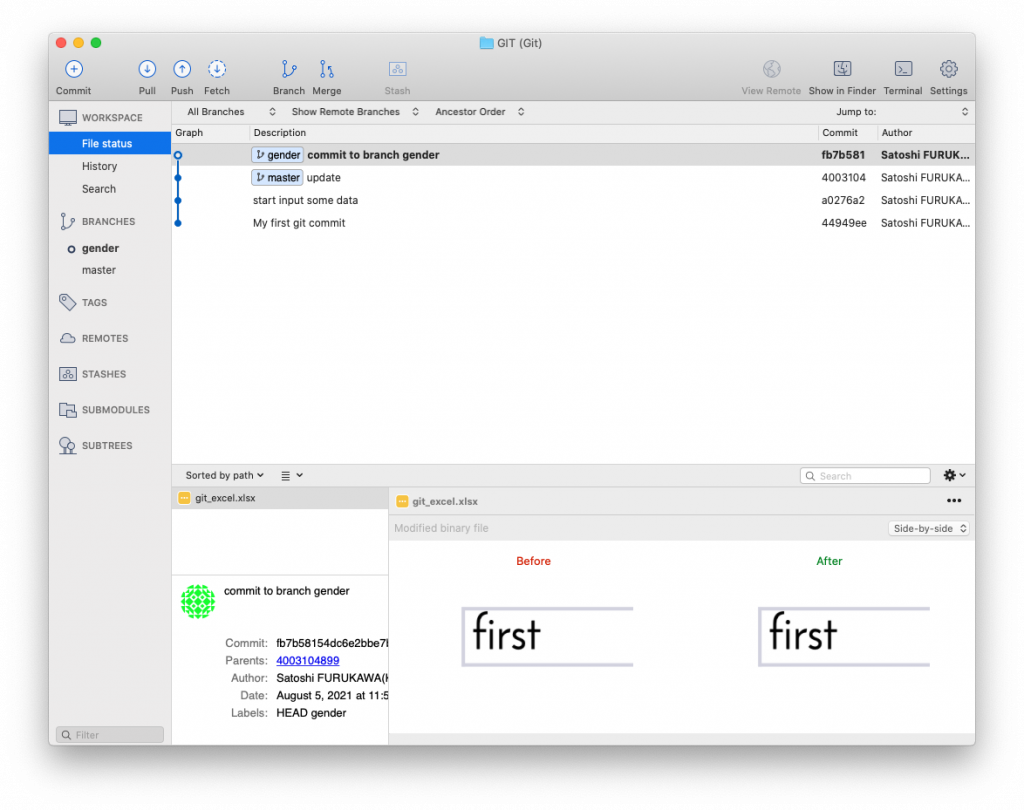
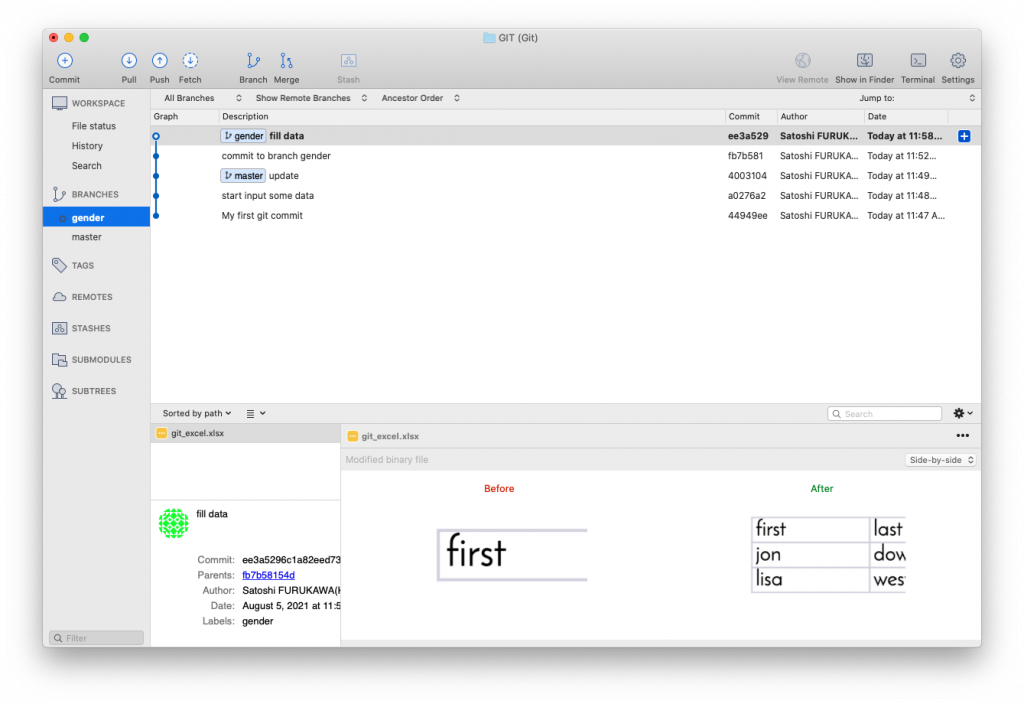
EXAMPLE: You are working on a project to input some data to an Excel spreadsheet. You boss come and ask to add a new column [Gender] and input (F) or (M), so you follow the order. A few days later, your boss came again and ask to add other 2 columns [F] and [M], divide data [Gender] to [F] and [M], if it’s (F), input “1” to [F} column, if it’s (m), [M] to 1. So you worked on the devision. Next day, your boss come again and said bring back to [F] and [M] to [Gender] and a few days later… Things like this happen all the time, isn’t it.
If it’s simple(but stressful 😫) as the example, probably when you’ve asked to add the 2 columns, you save the current file as different file name as a backup before adding these, and you continue working on the same file. So list,exl and list-backup1.exl. But I’m pretty sure that your boss come again and ask more changes… and so on, You’ll make so many backups and alternative files, the project folder getting messy easily. Imagine if you are saving files at the Desktop… nightmare!! Also if are working with some other collaborators to share the folder or even a file together, it’s so hard to manage and track what’s going on in the project folder, what have been changed and by who.
The GUI (Graphic User Interface) is available for free, I recommend Sourcetree, available both Mac and Windows.
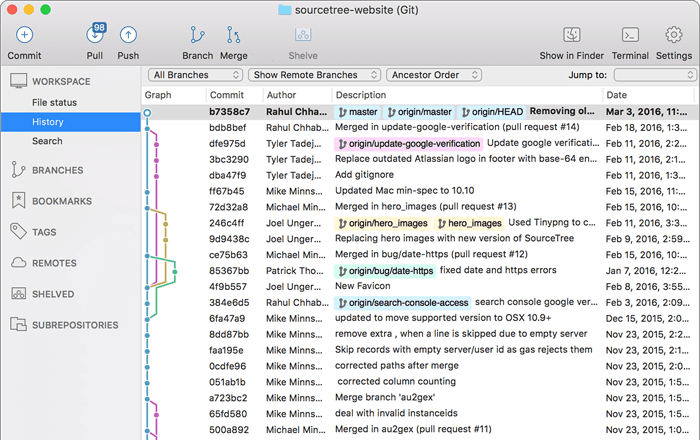
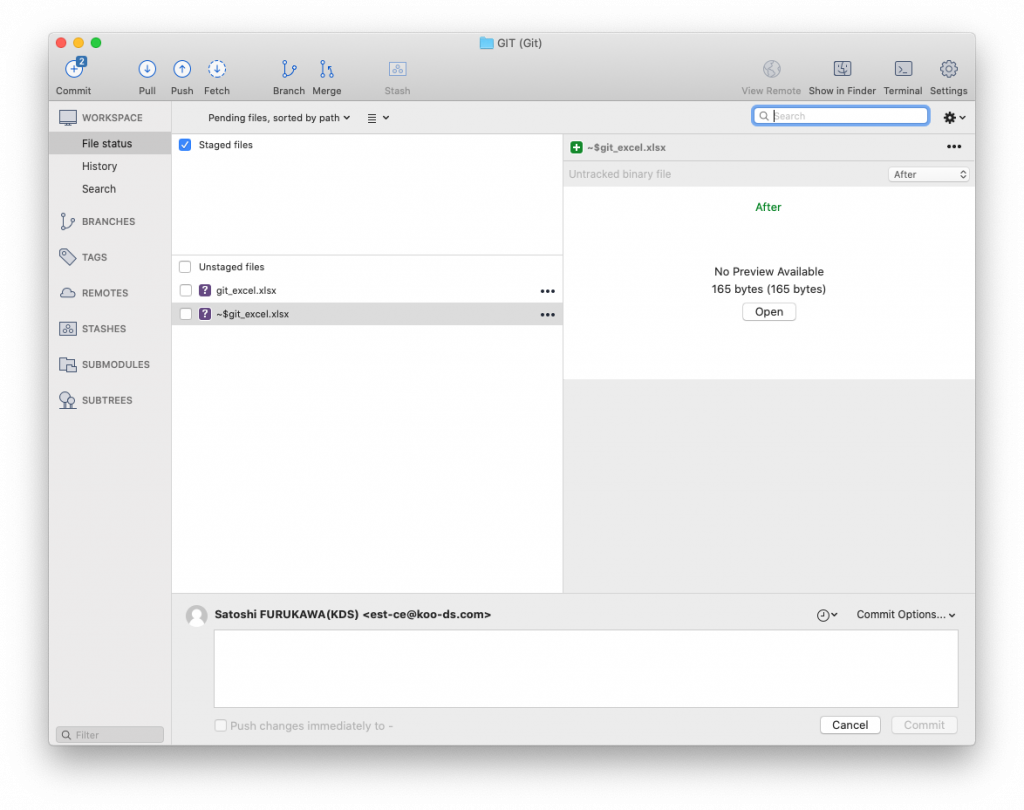
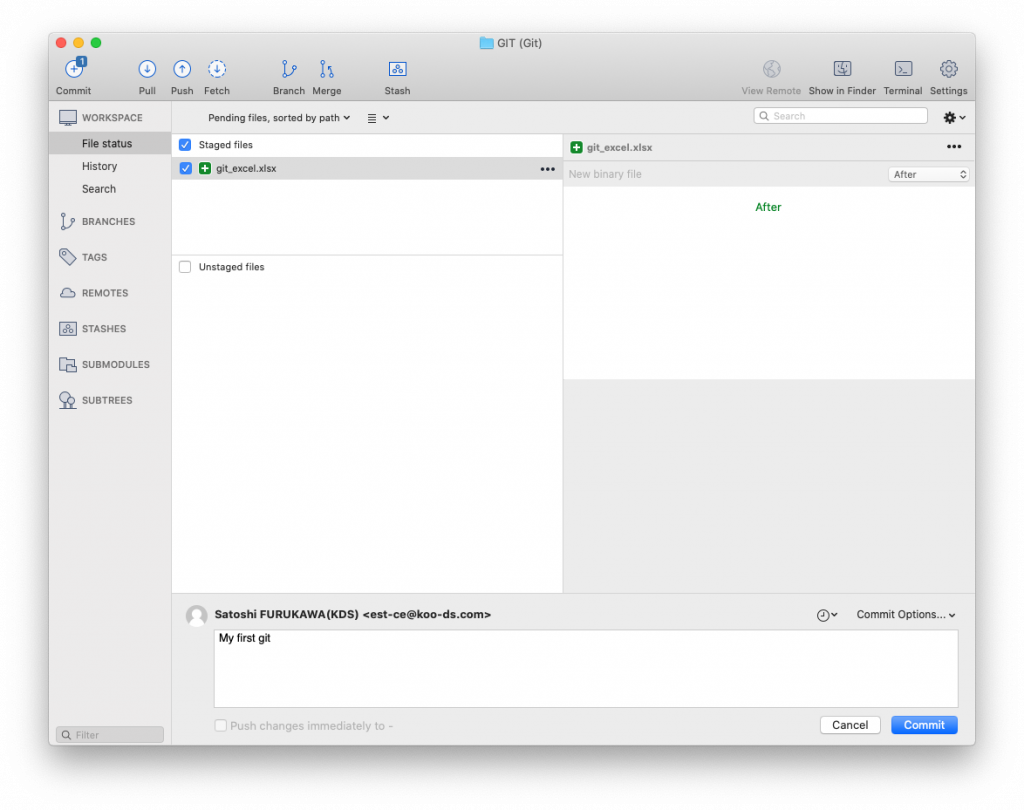
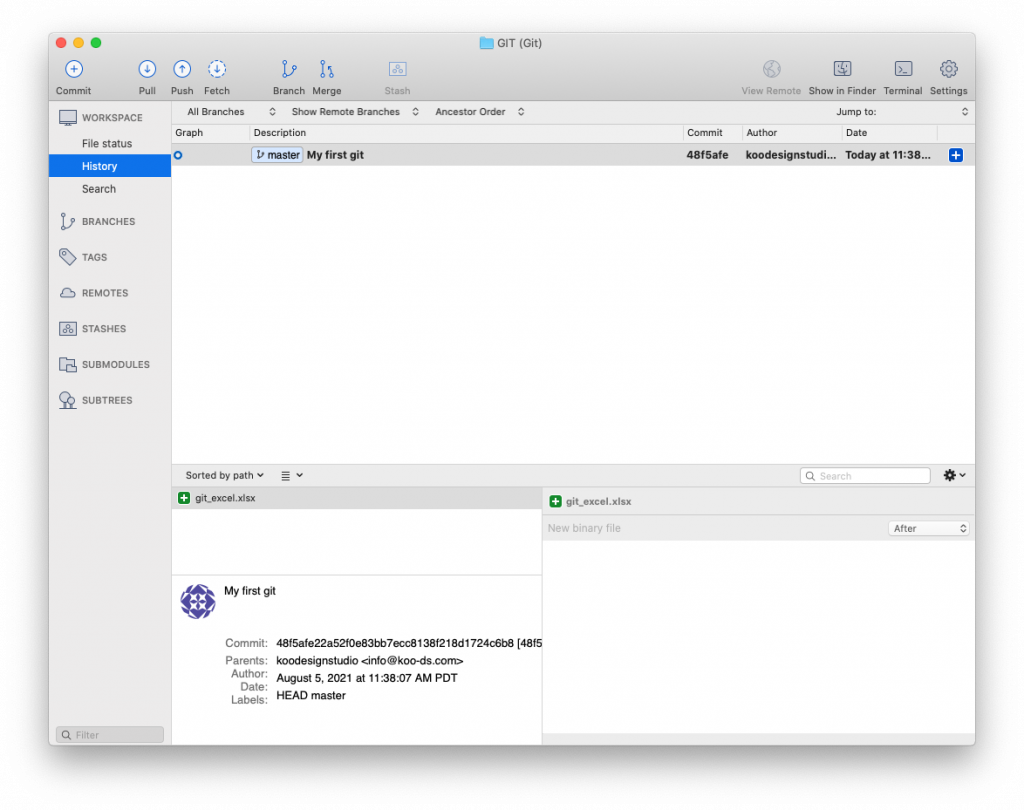
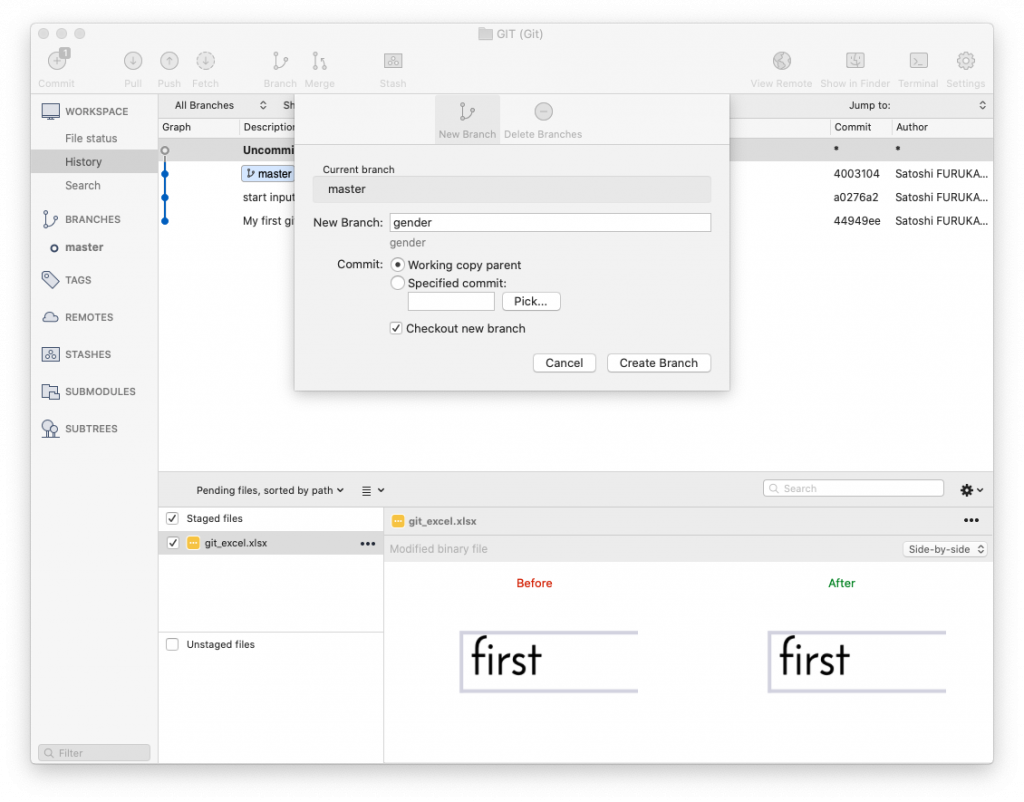
Working with collaborators using git is just amazing, you can work a same file with them at the same time and sync changes when you need to. or share your experiment with them etc..
GitHub is built for a remote git storage, storage called a “repository” in git, share a git repo to the world. You can download (git clone) to your computer (local) whatever uploaded to GitHub as public. And it can be shared ONLY for private too. GitHub has became so popular, maybe that’s why it sounds familiar to you too.
To work with remote git repository using Sourcetree,
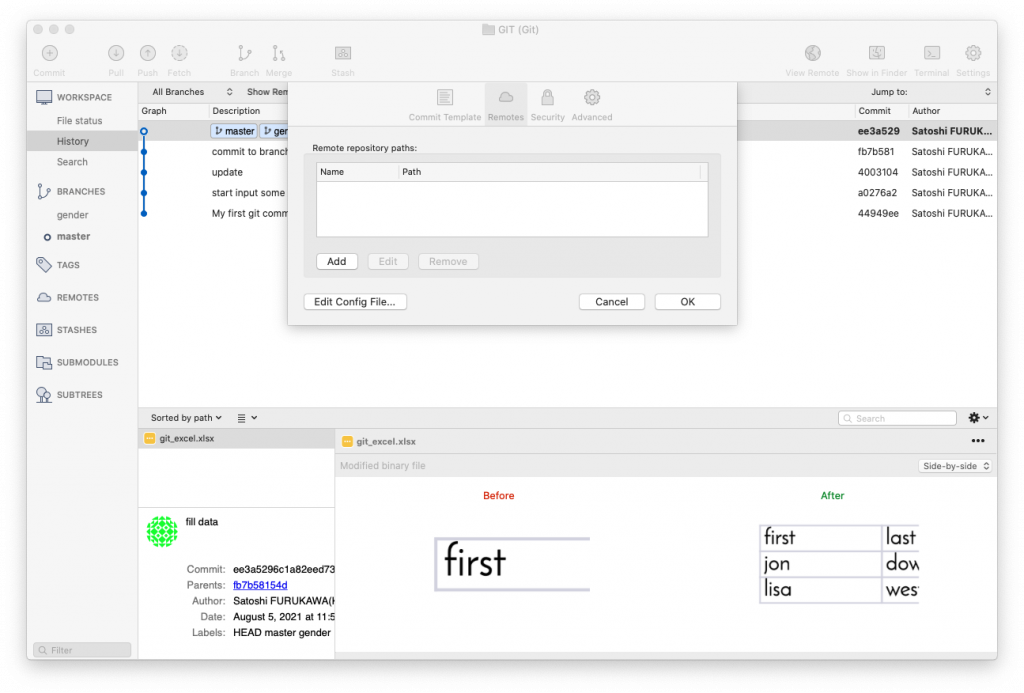
Type remote git name as “origin‘. Then URL/path “https://koo-ds.com:/data/git/GIT_TEST.git“, where you put the remote repository. If you push to GitHub, the option, select Host Type such as GitHub, Host Root URL will automatically filled as https://github.com, then type your GitHub Username. (when sourcetree try to connect to the remote server, it will ask you to type your username and password.)
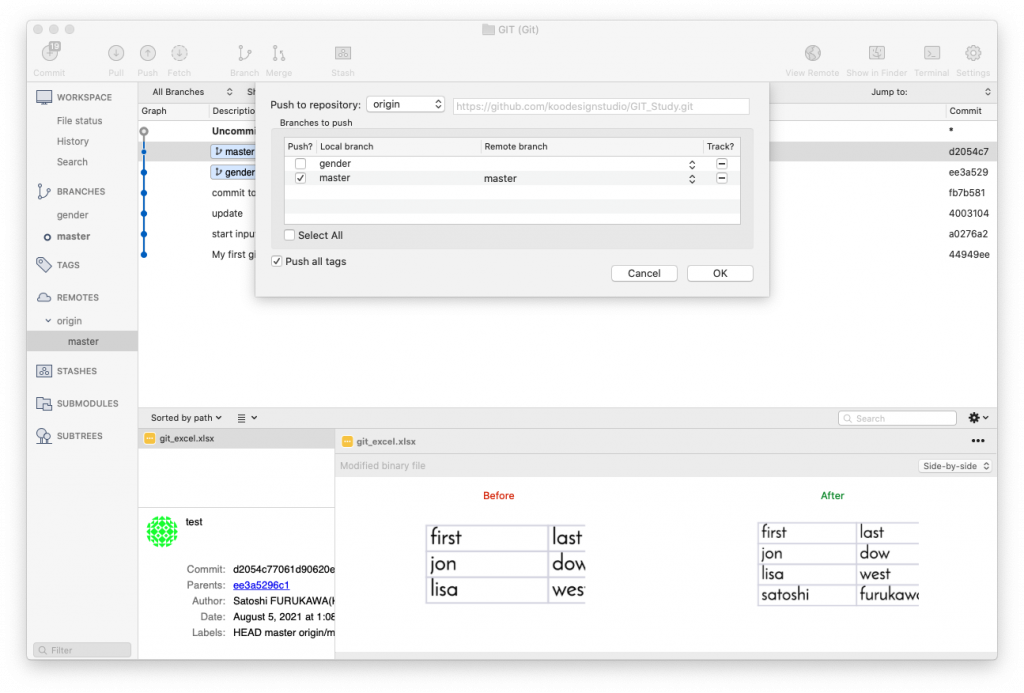
Now you can push your project to remote server, select REMOTES at the left and select your server where you want to access to, Then “Push” at the top bar. You can select what branch you want to upload. Then It will connect and send git data to the remote server. When you are working the project from different computer, start new and “clone” the data from the remote repo, then add all files to your new local git repo and commit, push back to the remote repo, then go back to you original computer and “Pull“ the changes to it. You can work with collaborator remotely do the same.
work => save file => git add all => commit => push THEN pull => work => save => git add all => commit => push =>…
If you use GitHub, there is GitHub desktop software available. https://desktop.github.com
If you are familiar with a command line shell, you can use CLI, here is some command note:
$ cd toProjectFolder
$ git init (make a git in a project folder)
$ git add . (add all the changes to git)
$ git commit -am "My first git" (commit)
$ ssh username@remote_server.com
@ remoteServer $ cd /where/your/gitRepo/willbe/
@ remoteServer $ git init projectName.git --bare
$ git remote add origin usrname@remote_server.com:/where/gitRepo/willbe.git (set a remote git repo, you should create “willbe.git” repo first, it can be just empty git)
$ git push --set-upstream origin master (push to the remote)
$ git branch gender (create a new branch)
$ git checkout gender (switch to the branch)
$ git add . (add saved files to the new git branch)
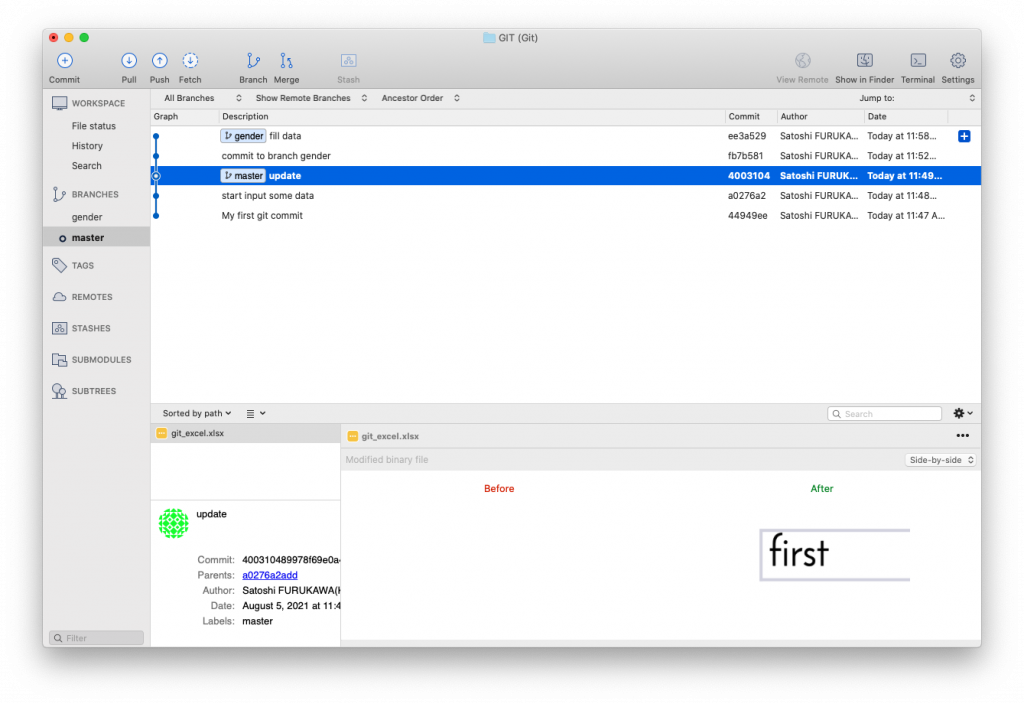
$ git checkout master (switch back to master)
$ git checkout gender (switch to gender again)
$ git push (you can push a branch to the remote repo too)
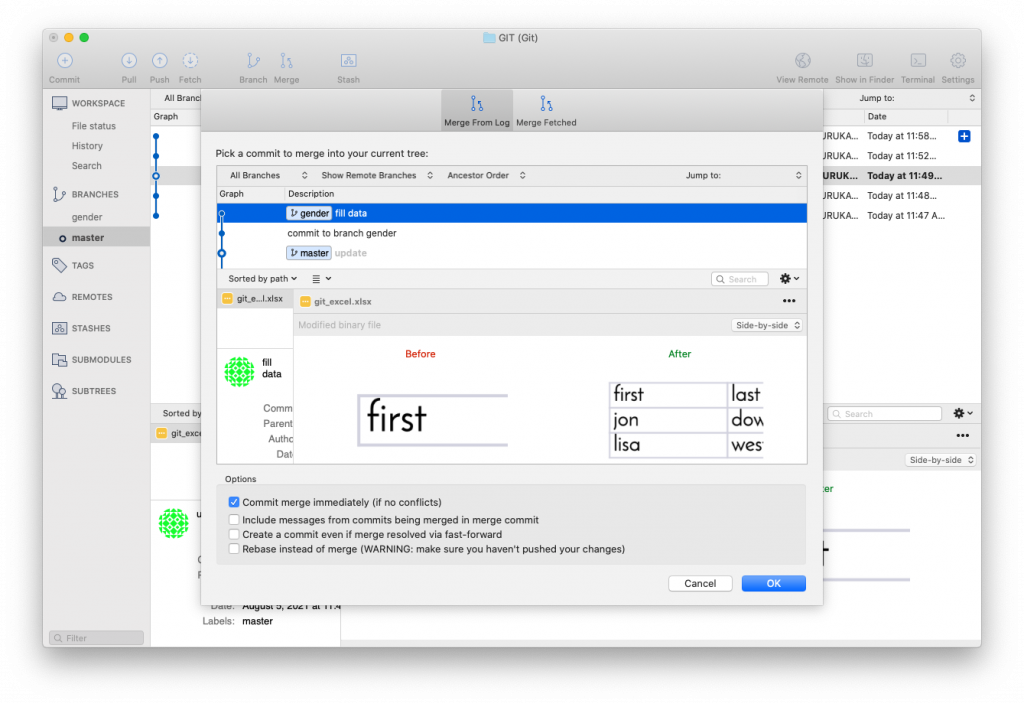
$ git checkout master (before you merge, go back to master)
$ git merge gender (merge all the changes you made and committed to gender branch to master)
$ git branch -d gender (delete gender branch)
$ git clone username@remote_server.com:/where/gitRepo/willbe.git (when you use different computer or your collaborator start to work remotely, download all the git project)
brew remove mysql
brew cleanup
sudo rm /usr/local/mysql
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/var/mysql
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/mysql*
sudo rm ~/Library/LaunchAgents/homebrew.mxcl.mysql.plist
sudo rm -rf /Library/StartupItems/MySQLCOM
sudo rm -rf /Library/PreferencePanes/MySql*
launchctl unload -w ~/Library/LaunchAgents/homebrew.mxcl.mysql.plist
rm -rf ~/Library/PreferencePanes/My*
sudo rm -rf /Library/Receipts/mysql*
sudo rm -rf /Library/Receipts/MySQL*
sudo rm -rf /private/var/db/receipts/*mysql*NOTE: download is free but you need to create your account first. Also download .dmg
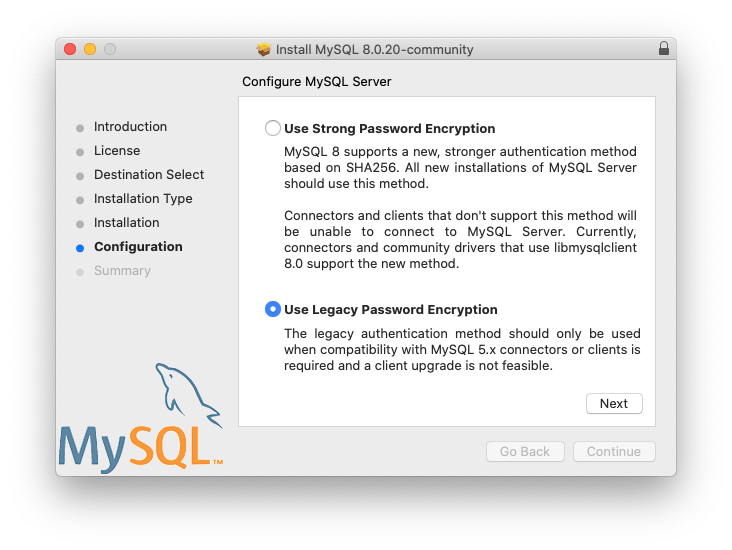
echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/usr/local/mysql/bin"' >> ~/.zprofile
source ~/.profile
mysql -u root (or your username) -phttps://dev.mysql.com/downloads/workbench/ go to Archive to select 6.3.10 (the latest version is for 11. Big Sur)
This is the 1st post.
This blog is about productions process, something I want to share with you things I’ve noticed through developing a content such as video, animation and web development.
I’ve installed WordPress in to my digitalocean.com server.
I had a hard time configure nginx to enable php. The reason was simply the PHP-FPM location. So when you configure, please make sure the path
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
include fastcgi.conf;
}